-
 Xi, Biden at Asia-Pacific summit under Trump trade war cloud
Xi, Biden at Asia-Pacific summit under Trump trade war cloud
-
India go on record six-hitting spree against South Africa

-
 France skipper Dupont says All Blacks 'back to their best'
France skipper Dupont says All Blacks 'back to their best'
-
Trump pressures US Senate with divisive cabinet picks

-
 Bagnaia strikes late in Barcelona practice to edge title rival Martin
Bagnaia strikes late in Barcelona practice to edge title rival Martin
-
High-ball hero Steward ready to 'front up' against South Africa

-
 Leader of Spain flood region admits 'mistakes'
Leader of Spain flood region admits 'mistakes'
-
Swiatek, Linette take Poland past Spain into BJK Cup quarter-finals

-
 Leftist voices seek to be heard at Rio's G20 summit
Leftist voices seek to be heard at Rio's G20 summit
-
Wales coach Jenkins urges players to 'get back on the horse'

-
 Zverev reaches ATP Finals last four, Alcaraz out
Zverev reaches ATP Finals last four, Alcaraz out
-
Boeing strike will hurt Ethiopian Airlines growth: CEO

-
 Springboks skipper Kolisi wary of England's 'gifted' Smith
Springboks skipper Kolisi wary of England's 'gifted' Smith
-
End of a love affair: news media quit X over 'disinformation'

-
 US finalizes up to $6.6 bn funding for chip giant TSMC
US finalizes up to $6.6 bn funding for chip giant TSMC
-
Scholz urges Ukraine talks in first call with Putin since 2022

-
 Zverev reaches ATP Finals last four, Alcaraz on brink of exit
Zverev reaches ATP Finals last four, Alcaraz on brink of exit
-
Lebanon rescuer picks up 'pieces' of father after Israel strike

-
 US retail sales lose steam in October after hurricanes
US retail sales lose steam in October after hurricanes
-
Zverev reaches ATP Finals last four with set win against Alcaraz

-
 Kerevi back for Australia against Wales, Suaalii on bench
Kerevi back for Australia against Wales, Suaalii on bench
-
Spate of child poisoning deaths sparks S.Africa xenophobia

-
 Comedian Conan O'Brien to host Oscars
Comedian Conan O'Brien to host Oscars
-
Rozner overtakes McIlroy and Hatton for Dubai lead

-
 Mourners bid farewell to medic killed in east Ukraine
Mourners bid farewell to medic killed in east Ukraine
-
Gore says 'absurd' to hold UN climate talks in petrostates

-
 Hamas says 'ready for ceasefire' as Israel presses Gaza campaign
Hamas says 'ready for ceasefire' as Israel presses Gaza campaign
-
Amorim says Man Utd is 'where I'm supposed to be'

-
 Japan hammer Indonesia to edge closer to World Cup spot
Japan hammer Indonesia to edge closer to World Cup spot
-
Jeff Beck guitar collection to go under the hammer in January

-
 Veteran Ranieri has 'no time for mistakes' on Roma return
Veteran Ranieri has 'no time for mistakes' on Roma return
-
Van Nistelrooy says he will 'cherish' Man Utd memories in farewell message

-
 IAEA chief tours sensitive Iran nuclear plants
IAEA chief tours sensitive Iran nuclear plants
-
Pompeii rejects 'mass tourism' with daily visitor limit

-
 Jailed Russian poet could be 'killed' in prison, warns wife
Jailed Russian poet could be 'killed' in prison, warns wife
-
French court orders release of Lebanese militant held since 1984

-
 Global stocks struggle after Fed signals slower rate cuts
Global stocks struggle after Fed signals slower rate cuts
-
UK economy slows, hitting government growth plans

-
 Primary schools empty as smog persists in Indian capital
Primary schools empty as smog persists in Indian capital
-
Palestinians turn to local soda in boycott of Israel-linked goods

-
 Typhoon Man-yi bears down on Philippines still reeling from Usagi
Typhoon Man-yi bears down on Philippines still reeling from Usagi
-
UK growth slows in third quarter, dealing blow to Labour government

-
 Chris Wood hits quickfire double in NZ World Cup qualifying romp
Chris Wood hits quickfire double in NZ World Cup qualifying romp
-
Markets struggle at end of tough week

-
 China tests building Moon base with lunar soil bricks
China tests building Moon base with lunar soil bricks
-
Film's 'search for Palestine' takes centre stage at Cairo festival

-
 Oil execs work COP29 as NGOs slam lobbyist presence
Oil execs work COP29 as NGOs slam lobbyist presence
-
Gore says climate progress 'won't slow much' because of Trump

-
 'Megaquake' warning hits Japan's growth
'Megaquake' warning hits Japan's growth
-
Stiff business: Berlin startup will freeze your corpse for monthly fee

| NGG | 0.27% | 62.54 | $ | |
| RBGPF | 2.67% | 61.84 | $ | |
| GSK | -2.43% | 33.195 | $ | |
| CMSC | 0.18% | 24.595 | $ | |
| RYCEF | 0.44% | 6.82 | $ | |
| RIO | 0.78% | 60.905 | $ | |
| VOD | 0.63% | 8.735 | $ | |
| CMSD | -0.07% | 24.34 | $ | |
| BCC | -0.42% | 139.765 | $ | |
| SCS | 0.3% | 13.31 | $ | |
| BTI | 2.35% | 36.345 | $ | |
| AZN | -2.43% | 63.5 | $ | |
| BCE | -0.11% | 26.81 | $ | |
| RELX | -3.45% | 44.418 | $ | |
| BP | -0.59% | 28.88 | $ | |
| JRI | -0.29% | 13.0391 | $ |

US company withdraws ALS drug after it fails in trial
Amylyx Pharmaceuticals announced Thursday it was withdrawing its approved treatment against the deadly neurodegenerative disease ALS after clinical data found no evidence the drug worked.
In a statement, the US company said it would discontinue its market authorizations for Relyvrio/Albrioza, using the brand names of the medicine in the US and Canadian markets.
"While this is a difficult moment for the ALS community, we reached this path forward in partnership with the stakeholders who will be impacted and in line with our steadfast commitment to people living with ALS and other neurodegenerative diseases," said the company's co-CEOs Joshua Cohen and Justin Klee in a statement.
The company also said it was reducing its workforce "by approximately 70 percent" as it focused on another experimental drug for use against ALS, and on repurposing Relyvrio for other conditions. It added it would continue to make Relyvrio available for patients who wish to keep using the treatment, through a "free drug program."
The news follows data from a clinical trial of 664 ALS patients announced in March, which found no significant differences in outcomes between those on the treatment group and those who received a placebo.
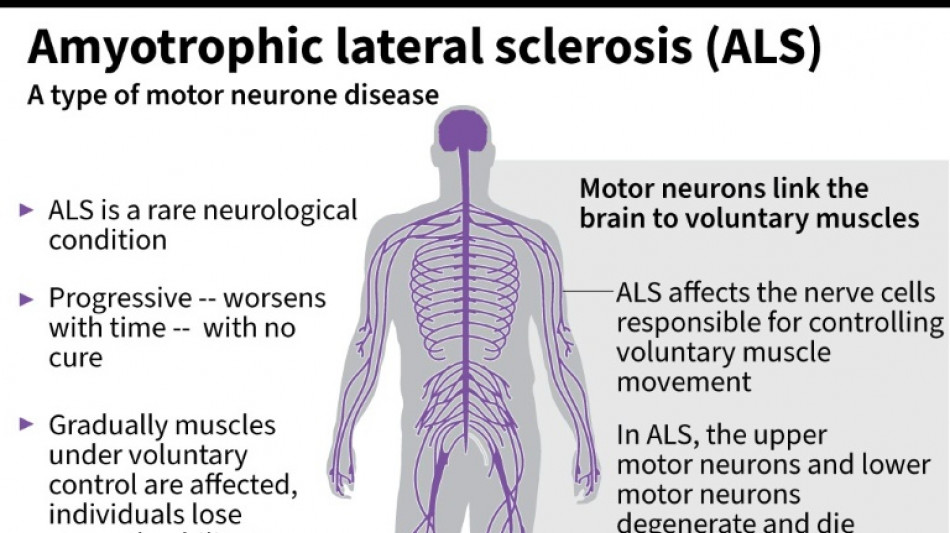
It was a big blow for patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, sometimes called Lou Gehrig's disease after the famous baseball player, which devastates nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord.
ALS affects about two people per 100,000 every year, causing progressive loss of motor and cognitive function. Most patients die within five years of their diagnosis.
Relyvrio's approval by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2022 was controversial and based on the results of a single trial that involved just 137 participants.
The FDA itself noted there was "residual uncertainty about the evidence of effectiveness" -- but "given the serious and life-threatening nature of ALS and the substantial unmet need, this level of uncertainty is acceptable in this instance and consideration of these results in the context of regulatory flexibility is appropriate."
- Patient groups backed approval -
Advocacy groups also mounted a major campaign sending a petition to the FDA with tens of thousands of signatures urging approval. Once it became available, Amylyx reportedly announced an eye-watering list price of $158,000 per year in the US, drawing criticism.
Patient groups in Europe watched with desperation at the bureaucratic delays.
When the European Union drug watchdog later announced it was rejecting Relyvrio, the decision was slammed as "an affront" by angry French patients, who say they "don't have time to wait." France later relented, offering conditional approval in November.
"We commend Amylyx for pulling Relyvrio off the market, while still ensuring that people living with ALS can access the drug if they believe it is helping them," said the US-based ALS association, which had lobbied for the drug's approval and funded its research.
"Safe and potentially effective treatments can be made accessible rapidly until further research can confirm their efficacy," it added.
For now, there remain only a handful of treatments available.
Riluzole, FDA approved in 1995, prolongs life approximately three months. Edaravone, FDA approved in 2017, has been found to slow disease progression and improve survival.
And in 2023, the regulatory body approved tofersen, a gene therapy treatment that targets those ALS cases that are caused by mutations in the SOD1 gene.
Th.Gonzalez--AT




