-
 Taylor holds off bloodied Serrano to retain undisputed crown
Taylor holds off bloodied Serrano to retain undisputed crown
-
Japan PM expresses concern to Xi over South China Sea situation

-
 Tens of thousands flee as Super Typhoon Man-yi nears Philippines
Tens of thousands flee as Super Typhoon Man-yi nears Philippines
-
Hoilett gives Canada win in Suriname as Mexico lose to Honduras

-
 Davis, James spark Lakers over Spurs while Cavs stay perfect
Davis, James spark Lakers over Spurs while Cavs stay perfect
-
Mushroom houses for Gaza? Arab designers offer home-grown innovations

-
 Gabon votes on new constitution hailed by junta as 'turning point'
Gabon votes on new constitution hailed by junta as 'turning point'
-
Young Libyans gear up for their first ever election

-
 Vice tightens around remaining civilians in eastern Ukraine
Vice tightens around remaining civilians in eastern Ukraine
-
Dutch coalition survives political turmoil after minister's resignation

-
 Uruguay end winless run with dramatic late win over Colombia
Uruguay end winless run with dramatic late win over Colombia
-
Max potential: 10 years since a teenage Verstappen wowed in Macau

-
 Tens of thousands flee as Typhoon Man-yi nears Philippines
Tens of thousands flee as Typhoon Man-yi nears Philippines
-
Is Argentina's Milei on brink of leaving Paris climate accord?

-
 Big Bang: Trump and Musk could redefine US space strategy
Big Bang: Trump and Musk could redefine US space strategy
-
Revolution over but more protests than ever in Bangladesh

-
 Minister resigns but Dutch coalition remains in place
Minister resigns but Dutch coalition remains in place
-
Ireland won 'ugly', says relieved Farrell

-
 Stirring 'haka' dance disrupts New Zealand's parliament
Stirring 'haka' dance disrupts New Zealand's parliament
-
England's Hull grabs lead over No.1 Korda at LPGA Annika

-
 Kosovo players walk off in Romania after 'Serbia' chants, game abandoned
Kosovo players walk off in Romania after 'Serbia' chants, game abandoned
-
Kosovo players walk off in Romania game after 'Serbia' chants

-
 Lame-duck Biden tries to reassure allies as Trump looms
Lame-duck Biden tries to reassure allies as Trump looms
-
Nervy Irish edge Argentina in Test nailbiter

-
 Ronaldo at double as Portugal reach Nations League quarters, Spain win
Ronaldo at double as Portugal reach Nations League quarters, Spain win
-
Fitch upgrades Argentina debt rating amid economic pain

-
 Trump picks Doug Burgum as energy czar in new administration
Trump picks Doug Burgum as energy czar in new administration
-
Phone documentary details struggles of Afghan women under Taliban

-
 Ronaldo shines as Portugal rout Poland to reach Nations League last-eight
Ronaldo shines as Portugal rout Poland to reach Nations League last-eight
-
Spain beat Denmark to seal Nations League group win

-
 Former AFCON champions Ghana bow out as minnows Comoros qualify
Former AFCON champions Ghana bow out as minnows Comoros qualify
-
Poland, Britain reach BJK Cup quarter-finals

-
 At summit under Trump shadow, Xi and Biden signal turbulence ahead
At summit under Trump shadow, Xi and Biden signal turbulence ahead
-
Lebanon said studying US truce plan for Israel-Hezbollah war

-
 Xi warns against 'protectionism' at APEC summit under Trump cloud
Xi warns against 'protectionism' at APEC summit under Trump cloud
-
Nigerian UN nurse escapes jihadist kidnappers after six years

-
 India in record six-hitting spree to rout South Africa
India in record six-hitting spree to rout South Africa
-
George tells England to prepare for rugby 'war' against Springboks

-
 Pogba's Juve contract terminated despite doping ban reduction
Pogba's Juve contract terminated despite doping ban reduction
-
Ukraine slams Scholz after first call with Putin in two years

-
 Michael Johnson's Grand Slam Track series to have LA final
Michael Johnson's Grand Slam Track series to have LA final
-
Kagiyama, Yoshida put Japan on top at Finland Grand Prix

-
 Alcaraz eyeing triumphant Davis Cup farewell for Nadal after ATP Finals exit
Alcaraz eyeing triumphant Davis Cup farewell for Nadal after ATP Finals exit
-
Xi, Biden at Asia-Pacific summit under Trump trade war cloud

-
 India go on record six-hitting spree against South Africa
India go on record six-hitting spree against South Africa
-
France skipper Dupont says All Blacks 'back to their best'

-
 Trump pressures US Senate with divisive cabinet picks
Trump pressures US Senate with divisive cabinet picks
-
Bagnaia strikes late in Barcelona practice to edge title rival Martin

-
 High-ball hero Steward ready to 'front up' against South Africa
High-ball hero Steward ready to 'front up' against South Africa
-
Leader of Spain flood region admits 'mistakes'


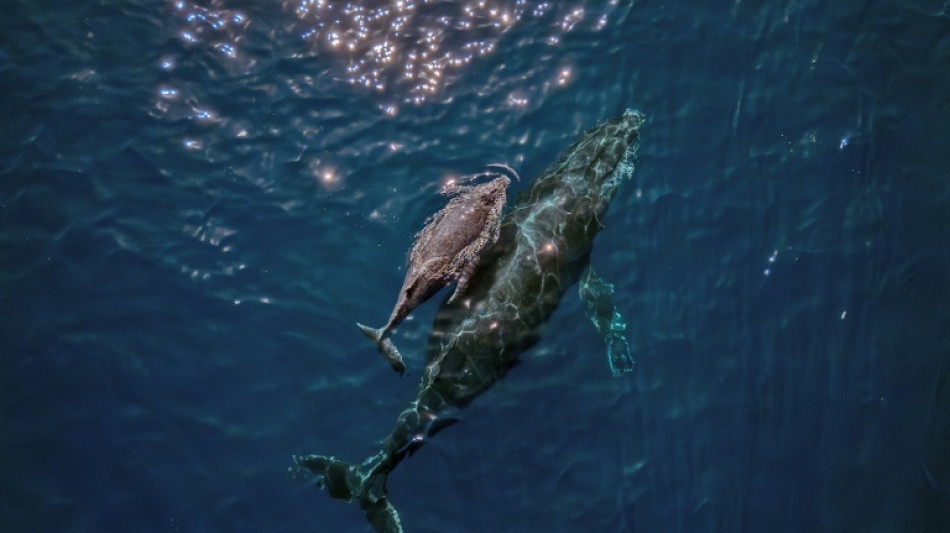
Whales 'cannot out-sing' human noise pollution
Baleen whales have evolved a special voice box to help them to sing underwater -- but this could also make them uniquely vulnerable to being drowned out by human noise pollution, according to new research published Wednesday.
Complex whale melodies, first recorded some 50 years ago, are known to play a key role in the social and reproductive communication of these massive marine mammals.
While toothed whales have a nasal vocal organ, filter-feeding baleen whales use a larynx, although scientists had not figured out exactly how it created the vocalisations.
In a new study published in the journal Nature, a team of scientists in Denmark, Austria, and the United States examined the larynxes of three stranded baleen whales -- the sei, minke, and humpback species -- using scanning and modelling techniques to reconstruct how they produce sound.
They found several differences from land mammals, including a U-shaped structure instead of vocal cords, that allows them to generate their low-frequency songs.
"We've never seen this in any other animal," lead author Coen Elemans, professor of bioacoustics at the University of Southern Denmark, told AFP.
"This is a completely novel adaptation, and we think this allowed these large whales to make sound in the water while basically holding their breath."
But the scientists also found a potentially serious challenge for the whales: the struggle to make themselves heard over noise pollution from ships.
- No escape -
Computer models showed that baleen whale songs can travel long distances through water, but at a maximum depth of 100 metres (330 feet) and at a frequency of up to 300 Hz -- within the range noise made by shipping vessels.
This means that whales in a noisy ocean soundscape are essentially trying to talk across a busy motorway or at a loud party: the further away you are, the less you'll be able to hear, Elemans said.
"It's really sad that baleen whale vocalisations exactly overlap with the sounds we make, predominantly with shipping noise, and there is no way for the whales to sing louder, at a higher frequency, or deeper in the water," Elemans said.
"These animals really can't escape this, and we really need to mitigate the noise we make."
They cannot even dive down to escape the din.
The deeper they go, the greater the pressure which reduces the volume of air available for vocalising, said Joy Reidenberg, a professor at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, who was not involved in the study.
Noise pollution can force whales to change their behaviour, such as remaining silent until quiet returns, moving to another location, or trying to communicate over the noise –- the latter two requiring whales to exert extra energy, potentially weakening their body condition and affecting long-term survival, Reidenberg said.
She said that understanding whale vocalisations could aid conservation efforts by helping understand which depths are "critical habitats".
This is particularly important at mating sites where, depending on the season, noise pollution can disrupt reproduction.
"We must be smarter about when and where we put sound into the water," Reidenberg said.
Researchers say there is an urgent need to regulate underwater noise.
The harm goes beyond whales -- there is evidence that scores of marine species are negatively affected by underwater noise pollution, Melanie Lancaster, senior Arctic species specialist at the World Wildlife Fund, who was not involved in the study, told AFP.
"We know the most about marine mammals, which is why they feature so prominently, yet the impacts are much farther reaching, essentially impacting entire marine ecosystems," she said.
P.A.Mendoza--AT