-
 Rozner overtakes McIlroy and Hatton for Dubai lead
Rozner overtakes McIlroy and Hatton for Dubai lead
-
Mourners bid farewell to medic killed in east Ukraine

-
 Gore says 'absurd' to hold UN climate talks in petrostates
Gore says 'absurd' to hold UN climate talks in petrostates
-
Hamas says 'ready for ceasefire' as Israel presses Gaza campaign

-
 Amorim says Man Utd is 'where I'm supposed to be'
Amorim says Man Utd is 'where I'm supposed to be'
-
Japan hammer Indonesia to edge closer to World Cup spot

-
 Jeff Beck guitar collection to go under the hammer in January
Jeff Beck guitar collection to go under the hammer in January
-
Veteran Ranieri has 'no time for mistakes' on Roma return

-
 Van Nistelrooy says he will 'cherish' Man Utd memories in farewell message
Van Nistelrooy says he will 'cherish' Man Utd memories in farewell message
-
IAEA chief tours sensitive Iran nuclear plants

-
 Pompeii rejects 'mass tourism' with daily visitor limit
Pompeii rejects 'mass tourism' with daily visitor limit
-
Jailed Russian poet could be 'killed' in prison, warns wife

-
 French court orders release of Lebanese militant held since 1984
French court orders release of Lebanese militant held since 1984
-
Global stocks struggle after Fed signals slower rate cuts

-
 UK economy slows, hitting government growth plans
UK economy slows, hitting government growth plans
-
Primary schools empty as smog persists in Indian capital

-
 Palestinians turn to local soda in boycott of Israel-linked goods
Palestinians turn to local soda in boycott of Israel-linked goods
-
Typhoon Man-yi bears down on Philippines still reeling from Usagi

-
 UK growth slows in third quarter, dealing blow to Labour government
UK growth slows in third quarter, dealing blow to Labour government
-
Chris Wood hits quickfire double in NZ World Cup qualifying romp

-
 Markets struggle at end of tough week
Markets struggle at end of tough week
-
China tests building Moon base with lunar soil bricks

-
 Film's 'search for Palestine' takes centre stage at Cairo festival
Film's 'search for Palestine' takes centre stage at Cairo festival
-
Oil execs work COP29 as NGOs slam lobbyist presence

-
 Gore says climate progress 'won't slow much' because of Trump
Gore says climate progress 'won't slow much' because of Trump
-
'Megaquake' warning hits Japan's growth

-
 Stiff business: Berlin startup will freeze your corpse for monthly fee
Stiff business: Berlin startup will freeze your corpse for monthly fee
-
Wars, looming Trump reign set to dominate G20 summit

-
 Xi, Biden attend Asia-Pacific summit, prepare to meet
Xi, Biden attend Asia-Pacific summit, prepare to meet
-
Kyrgios to make competitive return at Brisbane next month after injuries

-
 Dominican Juan Luis Guerra triumphs at 25th annual Latin Grammys
Dominican Juan Luis Guerra triumphs at 25th annual Latin Grammys
-
Landslide win for Sri Lanka president's leftist coalition in snap polls

-
 Australian World Cup penalty hero Vine takes mental health break
Australian World Cup penalty hero Vine takes mental health break
-
As Philippines picks up from Usagi, a fresh storm bears down

-
 Tropical Storm Sara pounds Honduras with heavy rain
Tropical Storm Sara pounds Honduras with heavy rain
-
Pepi gives Pochettino win for USA in Jamaica

-
 'Hell to heaven' as China reignite World Cup hopes with late winner
'Hell to heaven' as China reignite World Cup hopes with late winner
-
Rebel attacks keep Indian-run Kashmir on the boil

-
 New Zealand challenge 'immense but fantastic' for France
New Zealand challenge 'immense but fantastic' for France
-
Under pressure England boss Borthwick in Springboks' spotlight

-
 All Blacks plan to nullify 'freakish' Dupont, says Lienert-Brown
All Blacks plan to nullify 'freakish' Dupont, says Lienert-Brown
-
TikTok makes AI driven ad tool available globally

-
 Japan growth slows as new PM readies stimulus
Japan growth slows as new PM readies stimulus
-
China retail sales pick up speed, beat forecasts in October

-
 Asian markets fluctuate at end of tough week
Asian markets fluctuate at end of tough week
-
Gay, trans people voicing -- and sometimes screaming -- Trump concerns

-
 Argentina fall in Paraguay, Brazil held in Venezuela
Argentina fall in Paraguay, Brazil held in Venezuela
-
N. Korean leader orders 'mass production' of attack drones

-
 Pakistan's policies hazy as it fights smog
Pakistan's policies hazy as it fights smog
-
Nature pays price for war in Israel's north


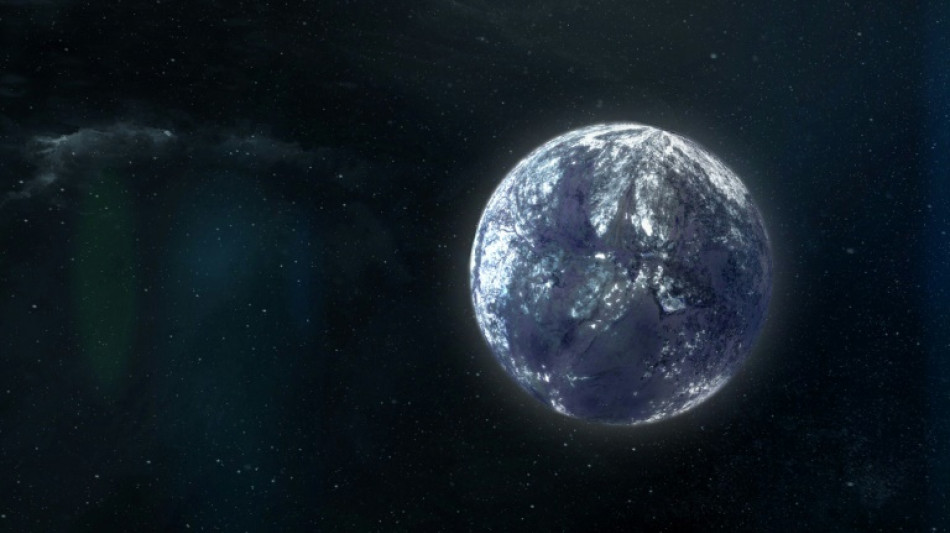
Starless and forever alone: more 'rogue' planets discovered
The Euclid space telescope has discovered seven more rogue planets, shining a light on the dark and lonely worlds floating freely through the universe untethered to any star.
Without being bound to a star, as the Earth is to the Sun, there are no days or years on these planets, which languish in perpetual night.
Yet scientists believe there is a chance they could be able to host life -- and estimate there may be trillions dotted throughout the Milky Way.
Last week the European Space Agency released the Euclid telescope's first scientific results since the mission launched in July.
Among the discoveries were seven new free-floating planets, gas giants at least four times the mass of Jupiter.
They were spotted in the Orion Nebula, the nearest star-forming region to Earth, roughly 1,500 light years away.
Euclid also confirmed the existence of dozens of other previously detected rogue planets.
Spanish astronomer Eduardo Martin, the lead author of a pre-print study published on arXiv.org Friday, said this was likely just the "tip of the iceberg".
Because they do not reflect the light of a star, spotting rogue planets is like "finding a needle in a haystack", Martin told AFP.
Younger planets, such as those discovered by Euclid, are hotter, making them a little easier to see.
- 'Awe and mystery' -
Some research has suggested there are around 20 rogue planets for every star, which could put their number in the trillions in our home galaxy alone.
Given there are thought to be hundreds of billions of galaxies across the universe, the potential number of free-floating worlds becomes difficult to fathom.
When NASA's Roman space telescope launches in 2027 it is expected find many more rogue planets, possibly offering clarity about how many could be out there.
Gavin Coleman, an astronomer at the Queen Mary University of London who was not involved in the Euclid research, said these strange worlds often evoked "feelings of awe and mystery".
"We've all grown up with the Sun in the sky, and so to think of a planet just drifting throughout space with no star on their horizon is fascinating," he told AFP.
But not all rogue planets wander alone. Four of the more than 20 confirmed by Euclid are believed to be binaries -- two planets orbiting each other in a single system.
- Could they host life? -
If rogue planets are habitable, they could be a key target in humanity's search for extraterrestrial life.
"Some of our closest neighbours are likely rogue planets," Martin said.
Lacking heat from a nearby star, free-floating planets are believed to be cold, with frozen surfaces.
That means any life-supporting energy would have to come from inside the planet.
Most of Neptune's energy comes from within, Coleman pointed out.
And geothermal vents allow animals to survive on Earth that have never seen the Sun's rays.
But even under the best conditions, this extreme isolation would likely be able to support only bacterial and microbial life, Coleman said.
- Advantage of being alone -
Rogue planets could be thought of as traversing a lonely path through the cosmos.
But "being around a star has its downsides", said study co-author Christopher Conselice, professor of extragalactic astronomy at the UK's University of Manchester.
One particular downside comes to mind.
Once the Sun becomes a red giant -- in an estimated 7.6 billion years -- it will greatly expand, swallowing the Earth.
Rogue planets do not have to worry about eventually being destroyed by a star. "These things will last forever," Conselice told AFP.
"If you don't mind the cold temperatures you could survive on these planets for eternity."
The Euclid study also offered clues to how rogue planets are created, Conselice said.
Some could be formed in the outer part of a solar system before getting detached from their star and floating away.
But the study indicates that many rogue planets may be created as a "natural byproduct" of the star-formation process, he said.
This suggests a "really close connection between stars and planets and how they form", he said.
"There's no firm answers yet," he added.
H.Thompson--AT