-
 China tests building Moon base with lunar soil bricks
China tests building Moon base with lunar soil bricks
-
Film's 'search for Palestine' takes centre stage at Cairo festival

-
 Oil execs work COP29 as NGOs slam lobbyist presence
Oil execs work COP29 as NGOs slam lobbyist presence
-
Gore says climate progress 'won't slow much' because of Trump

-
 'Megaquake' warning hits Japan's growth
'Megaquake' warning hits Japan's growth
-
Stiff business: Berlin startup will freeze your corpse for monthly fee

-
 Wars, looming Trump reign set to dominate G20 summit
Wars, looming Trump reign set to dominate G20 summit
-
Xi, Biden attend Asia-Pacific summit, prepare to meet

-
 Kyrgios to make competitive return at Brisbane next month after injuries
Kyrgios to make competitive return at Brisbane next month after injuries
-
Dominican Juan Luis Guerra triumphs at 25th annual Latin Grammys

-
 Landslide win for Sri Lanka president's leftist coalition in snap polls
Landslide win for Sri Lanka president's leftist coalition in snap polls
-
Australian World Cup penalty hero Vine takes mental health break

-
 As Philippines picks up from Usagi, a fresh storm bears down
As Philippines picks up from Usagi, a fresh storm bears down
-
Tropical Storm Sara pounds Honduras with heavy rain

-
 Pepi gives Pochettino win for USA in Jamaica
Pepi gives Pochettino win for USA in Jamaica
-
'Hell to heaven' as China reignite World Cup hopes with late winner

-
 Rebel attacks keep Indian-run Kashmir on the boil
Rebel attacks keep Indian-run Kashmir on the boil
-
New Zealand challenge 'immense but fantastic' for France

-
 Under pressure England boss Borthwick in Springboks' spotlight
Under pressure England boss Borthwick in Springboks' spotlight
-
All Blacks plan to nullify 'freakish' Dupont, says Lienert-Brown

-
 TikTok makes AI driven ad tool available globally
TikTok makes AI driven ad tool available globally
-
Japan growth slows as new PM readies stimulus

-
 China retail sales pick up speed, beat forecasts in October
China retail sales pick up speed, beat forecasts in October
-
Asian markets fluctuate at end of tough week

-
 Gay, trans people voicing -- and sometimes screaming -- Trump concerns
Gay, trans people voicing -- and sometimes screaming -- Trump concerns
-
Argentina fall in Paraguay, Brazil held in Venezuela

-
 N. Korean leader orders 'mass production' of attack drones
N. Korean leader orders 'mass production' of attack drones
-
Pakistan's policies hazy as it fights smog

-
 Nature pays price for war in Israel's north
Nature pays price for war in Israel's north
-
New Zealand's prolific Williamson back for England Test series

-
 Mexico City youth grapple with growing housing crisis
Mexico City youth grapple with growing housing crisis
-
After Trump's victory, US election falsehoods shift left

-
 Cracks deepen in Canada's pro-immigration 'consensus'
Cracks deepen in Canada's pro-immigration 'consensus'
-
Xi inaugurates South America's first Chinese-funded port in Peru

-
 Tyson slaps Paul in final face-off before Netflix bout
Tyson slaps Paul in final face-off before Netflix bout
-
England wrap-up T20 series win over West Indies

-
 Stewards intervene to stop Israel, France football fans clash at Paris match
Stewards intervene to stop Israel, France football fans clash at Paris match
-
Special counsel hits pause on Trump documents case

-
 Japan's Princess Mikasa, great aunt to emperor, dies aged 101
Japan's Princess Mikasa, great aunt to emperor, dies aged 101
-
Cricket at 2028 Olympics could be held outside Los Angeles

-
 Trump names vaccine skeptic RFK Jr. to head health dept
Trump names vaccine skeptic RFK Jr. to head health dept
-
Ye claims 'Jews' controlling Kardashian clan: lawsuit

-
 Japan into BJK Cup quarter-finals as Slovakia stun USA
Japan into BJK Cup quarter-finals as Slovakia stun USA
-
Sri Lanka president's party headed for landslide: early results

-
 Olympics 'above politics' say LA 2028 organisers after Trump win
Olympics 'above politics' say LA 2028 organisers after Trump win
-
Panic strikes Port-au-Prince as residents flee gang violence

-
 Carsley hails England's strength in depth as understudies sink Greece
Carsley hails England's strength in depth as understudies sink Greece
-
Undefeated Chiefs lose kicker Butker to knee injury

-
 Wallabies winger Vunivalu signs for La Rochelle
Wallabies winger Vunivalu signs for La Rochelle
-
Musk met Iran UN ambassador on defusing tension under Trump: NYT

| SCS | -0.75% | 13.27 | $ | |
| NGG | 0.4% | 62.37 | $ | |
| CMSC | -0.24% | 24.55 | $ | |
| RIO | -0.31% | 60.43 | $ | |
| BP | 1.65% | 29.05 | $ | |
| BTI | 0.2% | 35.49 | $ | |
| CMSD | -0.02% | 24.725 | $ | |
| BCC | -1.57% | 140.35 | $ | |
| RBGPF | 100% | 61.84 | $ | |
| AZN | -0.38% | 65.04 | $ | |
| RYCEF | -4.71% | 6.79 | $ | |
| RELX | -0.37% | 45.95 | $ | |
| BCE | -1.38% | 26.84 | $ | |
| GSK | -2.09% | 34.39 | $ | |
| JRI | -0.23% | 13.21 | $ | |
| VOD | -0.81% | 8.68 | $ |

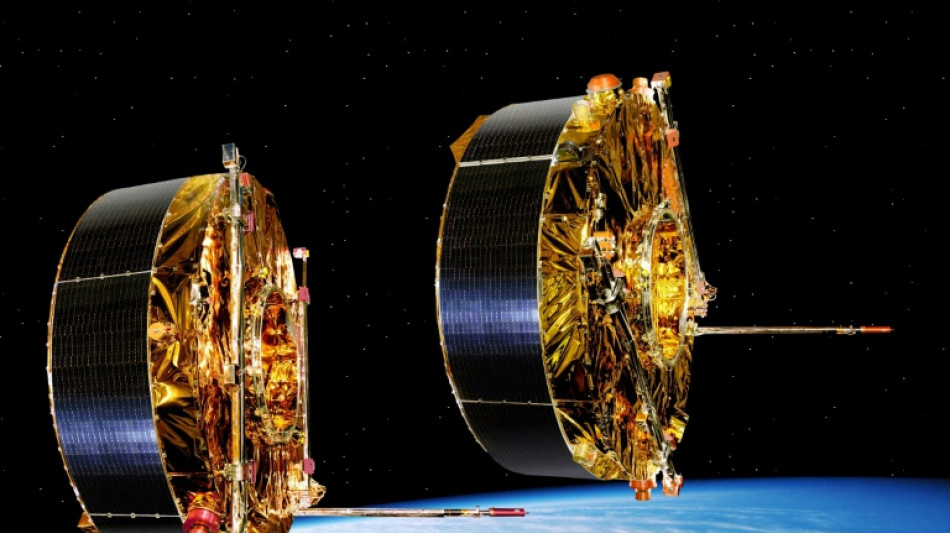
Old satellite to burn up over Pacific in 'targeted' re-entry first
After 24 years diligently studying Earth's magnetic field, a satellite will mostly burn up over the Pacific Ocean on Sunday during a "targeted" re-entry into the atmosphere, in a first for the European Space Agency as it seeks to reduce space debris.
Since launching in 2000, the Salsa satellite has helped shed light on the magnetosphere, the powerful magnetic shield that protects Earth from solar winds -- and without which the planet would be uninhabitable.
According to the ESA, Salsa's return home will mark the first-ever "targeted" re-entry for a satellite, which means it will fall back to Earth at a specific time and place but will not be controlled as it re-enters the atmosphere.
Teams on the ground have already performed a series of manoeuvres with the 550-kilogram (1,200-pound) satellite to ensure it burns up over a remote and uninhabited region of the South Pacific, off the coast of Chile.
This unique re-entry is possible because of Salsa's unusual oval-shaped orbit. During its swing around the planet, which takes two and half days, the satellite strays as far as 130,000 kilometres (80,000 miles), and comes as close as just a few hundred kilometres.
Bruno Sousa, head of the ESA's inner solar system missions operations unit, said it had been crucial that Salsa came within roughly 110 kilometres during its last two orbits.
"Then immediately on the next orbit, it would come down at 80 kilometres, which is the region in space already within the atmosphere, where we have the highest chance (for it) to be fully captured and burned," he told a press conference.
When a satellite starts entering the atmosphere at around 100 kilometres above sea level, intense friction with atmospheric particles -- and the heat this causes -- starts making them disintegrate.
But some fragments can still make it back down to Earth.
- Fear of 'cascading' space junk -
The ESA is hoping to pinpoint where Salsa, roughly the size of a small car, re-enters the atmosphere to within a few hundred metres.
Because the satellite is so old, it does not have fancy new tech -- like a recording device -- making tracking this part tricky.
A plane will be flying at an altitude of 10 kilometres to watch the satellite burn up -- and track its falling debris, which is expected to be just 10 percent of its original mass.
Salsa is just one of four satellites that make up the ESA's Cluster mission, which is coming to an end. The other three are scheduled for a similar fate in 2025 and 2026.
The ESA hopes to learn from these re-entries which type of materials do not burn up in the atmosphere, so that "in the future we can build satellites that can be totally evaporated by this process," Sousa said.
Scientists have been sounding the alarm about space junk, which is the debris left by the enormous number of dead satellites and other missions that continue orbiting our planet.
Last year the ESA signed a "zero debris" charter for its missions from 2030.
There are two main risks from space junk, according to the ESA's space debris system engineer Benjamin Bastida Virgili.
"One is that in orbit, you have the risk that your operational satellite collides with a piece of space debris, and that creates a cascading effect and generates more debris, which would then put in risk other missions," he said.
The second comes when the old debris re-enters the atmosphere, which happens almost daily as dead satellite fragments or rocket parts fall back to Earth.
Designing satellites that completely burn up in the atmosphere will mean there is "no risk for the population," Bastida Virgili emphasised.
But there is little cause for alarm. According to the ESA, the chance of a piece of space debris injuring someone on the ground is less than one in a hundred billion.
This is 65,000 times lower than the odds of being struck by lightning.
G.P.Martin--AT