-
 Markets struggle at end of tough week
Markets struggle at end of tough week
-
China tests building Moon base with lunar soil bricks

-
 Film's 'search for Palestine' takes centre stage at Cairo festival
Film's 'search for Palestine' takes centre stage at Cairo festival
-
Oil execs work COP29 as NGOs slam lobbyist presence

-
 Gore says climate progress 'won't slow much' because of Trump
Gore says climate progress 'won't slow much' because of Trump
-
'Megaquake' warning hits Japan's growth

-
 Stiff business: Berlin startup will freeze your corpse for monthly fee
Stiff business: Berlin startup will freeze your corpse for monthly fee
-
Wars, looming Trump reign set to dominate G20 summit

-
 Xi, Biden attend Asia-Pacific summit, prepare to meet
Xi, Biden attend Asia-Pacific summit, prepare to meet
-
Kyrgios to make competitive return at Brisbane next month after injuries

-
 Dominican Juan Luis Guerra triumphs at 25th annual Latin Grammys
Dominican Juan Luis Guerra triumphs at 25th annual Latin Grammys
-
Landslide win for Sri Lanka president's leftist coalition in snap polls

-
 Australian World Cup penalty hero Vine takes mental health break
Australian World Cup penalty hero Vine takes mental health break
-
As Philippines picks up from Usagi, a fresh storm bears down

-
 Tropical Storm Sara pounds Honduras with heavy rain
Tropical Storm Sara pounds Honduras with heavy rain
-
Pepi gives Pochettino win for USA in Jamaica

-
 'Hell to heaven' as China reignite World Cup hopes with late winner
'Hell to heaven' as China reignite World Cup hopes with late winner
-
Rebel attacks keep Indian-run Kashmir on the boil

-
 New Zealand challenge 'immense but fantastic' for France
New Zealand challenge 'immense but fantastic' for France
-
Under pressure England boss Borthwick in Springboks' spotlight

-
 All Blacks plan to nullify 'freakish' Dupont, says Lienert-Brown
All Blacks plan to nullify 'freakish' Dupont, says Lienert-Brown
-
TikTok makes AI driven ad tool available globally

-
 Japan growth slows as new PM readies stimulus
Japan growth slows as new PM readies stimulus
-
China retail sales pick up speed, beat forecasts in October

-
 Asian markets fluctuate at end of tough week
Asian markets fluctuate at end of tough week
-
Gay, trans people voicing -- and sometimes screaming -- Trump concerns

-
 Argentina fall in Paraguay, Brazil held in Venezuela
Argentina fall in Paraguay, Brazil held in Venezuela
-
N. Korean leader orders 'mass production' of attack drones

-
 Pakistan's policies hazy as it fights smog
Pakistan's policies hazy as it fights smog
-
Nature pays price for war in Israel's north

-
 New Zealand's prolific Williamson back for England Test series
New Zealand's prolific Williamson back for England Test series
-
Mexico City youth grapple with growing housing crisis

-
 After Trump's victory, US election falsehoods shift left
After Trump's victory, US election falsehoods shift left
-
Cracks deepen in Canada's pro-immigration 'consensus'

-
 Xi inaugurates South America's first Chinese-funded port in Peru
Xi inaugurates South America's first Chinese-funded port in Peru
-
Tyson slaps Paul in final face-off before Netflix bout

-
 England wrap-up T20 series win over West Indies
England wrap-up T20 series win over West Indies
-
Stewards intervene to stop Israel, France football fans clash at Paris match

-
 Special counsel hits pause on Trump documents case
Special counsel hits pause on Trump documents case
-
Japan's Princess Mikasa, great aunt to emperor, dies aged 101

-
 Cricket at 2028 Olympics could be held outside Los Angeles
Cricket at 2028 Olympics could be held outside Los Angeles
-
Trump names vaccine skeptic RFK Jr. to head health dept

-
 Ye claims 'Jews' controlling Kardashian clan: lawsuit
Ye claims 'Jews' controlling Kardashian clan: lawsuit
-
Japan into BJK Cup quarter-finals as Slovakia stun USA

-
 Sri Lanka president's party headed for landslide: early results
Sri Lanka president's party headed for landslide: early results
-
Olympics 'above politics' say LA 2028 organisers after Trump win

-
 Panic strikes Port-au-Prince as residents flee gang violence
Panic strikes Port-au-Prince as residents flee gang violence
-
Carsley hails England's strength in depth as understudies sink Greece

-
 Undefeated Chiefs lose kicker Butker to knee injury
Undefeated Chiefs lose kicker Butker to knee injury
-
Wallabies winger Vunivalu signs for La Rochelle

| RBGPF | 100% | 61.84 | $ | |
| RYCEF | -4.71% | 6.79 | $ | |
| CMSC | -0.24% | 24.55 | $ | |
| NGG | 0.4% | 62.37 | $ | |
| BCC | -1.57% | 140.35 | $ | |
| GSK | -2.09% | 34.39 | $ | |
| RIO | -0.31% | 60.43 | $ | |
| CMSD | -0.02% | 24.725 | $ | |
| AZN | -0.38% | 65.04 | $ | |
| SCS | -0.75% | 13.27 | $ | |
| RELX | -0.37% | 45.95 | $ | |
| JRI | -0.23% | 13.21 | $ | |
| BP | 1.65% | 29.05 | $ | |
| VOD | -0.81% | 8.68 | $ | |
| BCE | -1.38% | 26.84 | $ | |
| BTI | 0.2% | 35.49 | $ |

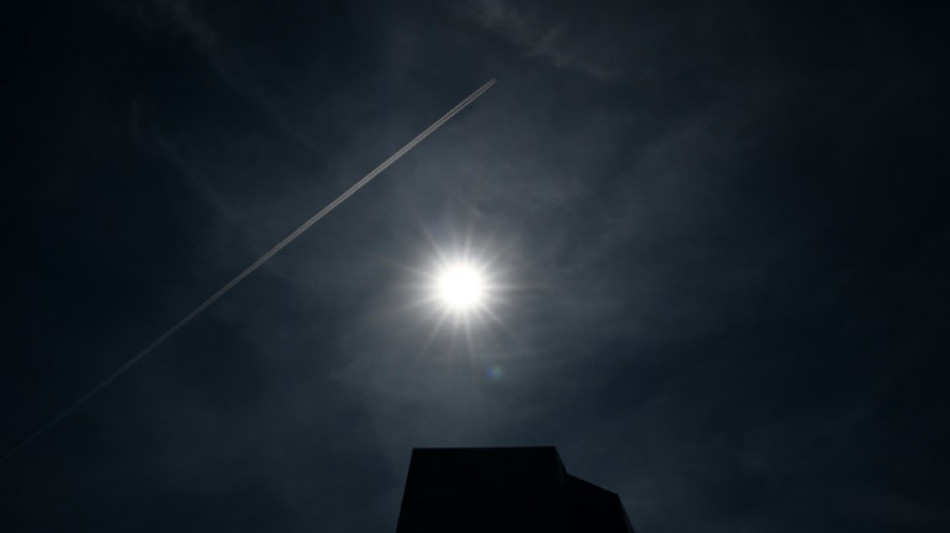
Plane contrails: white fluffy contributors to global warming
The white, feathery lines behind airplanes that look like bits of harmless cloud are anything but, warn experts, who say they could have a greater environmental impact than the aviation sector's CO2 emissions.
The condensation trails -- contrails, for short -- are being increasingly studied as scientists work with the industry to find technological solutions to the problem.
Classified as non-CO2 emissions from aircraft, in September they were the subject of a symposium in Montreal organized by the International Civil Aviation Organization, a UN agency.
- What are contrails? -
Contrails are clouds that form at high altitudes in cold, humid areas called ice supersaturated regions (ISSRs).
When jet fuel is burned by engines, water vapor condenses on to soot particles to form ice crystals.
Enough ice crystals, and they begin to form cirrus clouds -- high-altitude, wispy white filaments that, when created this way, trail out behind planes as they cross the sky.
These trails trap some of the heat that rises from the Earth at night, preventing it from radiating back out of the atmosphere -- thus acting as a greenhouse gas, causing warming, explains Donald Wuebbles, a professor at the University of Illinois.
Contrails that stay in the sky for a few minutes are not very worrisome, he says.
"But if they form at night, they'll maybe last a little longer, and at night they can cause a warming effect," he adds.
- What is the impact? -
Non-CO2 emissions could account for up to two-thirds of aviation's impact on global warming, which "gives you an idea of how important they are to consider," Wuebbles said.
And contrails could form up to 57 percent of that impact -- far more than the C02 emissions from burning fuel, according to a 2021 study.
However, such emissions are short-lived compared to carbon dioxide and their impact on global warming could be quickly eroded if solutions were found to avoid them, experts say.
- So what can be done? -
Not all flights create contrails -- it can depend on weather conditions and the aircraft's trajectory.
For example, at Air France, just four percent of flights are responsible for some 80 percent of the airline's contrail impact on global warming, notes Irene Boyer-Souchet, who is leading up the company's efforts to mitigate the damage.
The long-term strategy is to modify the trajectory of a fraction of flights.
Air France pilots made more than 3,000 observations over 18 months with the aim of helping Meteo-France improve its forecasts for at-risk areas so that pilots could eventually avoid them.
"The main risk is that by thinking you're avoiding an area, you could end up flying there because it's slightly off the weather forecast," Boyer-Souchet points out, illustrating the importance of fine-tuning the research.
Pilots from American Airlines conducted 70 test flights above or below at-risk areas, guided by satellite images, weather data, software models and AI prediction tools.
A 54-percent reduction in contrails was observed, along with a two-percent increase in fuel consumption.
Accelerating the deployment of a global contrail avoidance system could reduce aviation's impact on the climate by 40 percent, according to a Cambridge University report published in September.
The more flights in the air, however, the more complicated the implementation of such a system would be, notes Boyer-Souchet, who hopes that it will be a reality by 2030.
Th.Gonzalez--AT