-
 Kagiyama, Yoshida put Japan on top at Finland Grand Prix
Kagiyama, Yoshida put Japan on top at Finland Grand Prix
-
Alcaraz eyeing triumphant Davis Cup farewell for Nadal after ATP Finals exit

-
 Xi, Biden at Asia-Pacific summit under Trump trade war cloud
Xi, Biden at Asia-Pacific summit under Trump trade war cloud
-
India go on record six-hitting spree against South Africa

-
 France skipper Dupont says All Blacks 'back to their best'
France skipper Dupont says All Blacks 'back to their best'
-
Trump pressures US Senate with divisive cabinet picks

-
 Bagnaia strikes late in Barcelona practice to edge title rival Martin
Bagnaia strikes late in Barcelona practice to edge title rival Martin
-
High-ball hero Steward ready to 'front up' against South Africa

-
 Leader of Spain flood region admits 'mistakes'
Leader of Spain flood region admits 'mistakes'
-
Swiatek, Linette take Poland past Spain into BJK Cup quarter-finals

-
 Leftist voices seek to be heard at Rio's G20 summit
Leftist voices seek to be heard at Rio's G20 summit
-
Wales coach Jenkins urges players to 'get back on the horse'

-
 Zverev reaches ATP Finals last four, Alcaraz out
Zverev reaches ATP Finals last four, Alcaraz out
-
Boeing strike will hurt Ethiopian Airlines growth: CEO

-
 Springboks skipper Kolisi wary of England's 'gifted' Smith
Springboks skipper Kolisi wary of England's 'gifted' Smith
-
End of a love affair: news media quit X over 'disinformation'

-
 US finalizes up to $6.6 bn funding for chip giant TSMC
US finalizes up to $6.6 bn funding for chip giant TSMC
-
Scholz urges Ukraine talks in first call with Putin since 2022

-
 Zverev reaches ATP Finals last four, Alcaraz on brink of exit
Zverev reaches ATP Finals last four, Alcaraz on brink of exit
-
Lebanon rescuer picks up 'pieces' of father after Israel strike

-
 US retail sales lose steam in October after hurricanes
US retail sales lose steam in October after hurricanes
-
Zverev reaches ATP Finals last four with set win against Alcaraz

-
 Kerevi back for Australia against Wales, Suaalii on bench
Kerevi back for Australia against Wales, Suaalii on bench
-
Spate of child poisoning deaths sparks S.Africa xenophobia

-
 Comedian Conan O'Brien to host Oscars
Comedian Conan O'Brien to host Oscars
-
Rozner overtakes McIlroy and Hatton for Dubai lead

-
 Mourners bid farewell to medic killed in east Ukraine
Mourners bid farewell to medic killed in east Ukraine
-
Gore says 'absurd' to hold UN climate talks in petrostates

-
 Hamas says 'ready for ceasefire' as Israel presses Gaza campaign
Hamas says 'ready for ceasefire' as Israel presses Gaza campaign
-
Amorim says Man Utd is 'where I'm supposed to be'

-
 Japan hammer Indonesia to edge closer to World Cup spot
Japan hammer Indonesia to edge closer to World Cup spot
-
Jeff Beck guitar collection to go under the hammer in January

-
 Veteran Ranieri has 'no time for mistakes' on Roma return
Veteran Ranieri has 'no time for mistakes' on Roma return
-
Van Nistelrooy says he will 'cherish' Man Utd memories in farewell message

-
 IAEA chief tours sensitive Iran nuclear plants
IAEA chief tours sensitive Iran nuclear plants
-
Pompeii rejects 'mass tourism' with daily visitor limit

-
 Jailed Russian poet could be 'killed' in prison, warns wife
Jailed Russian poet could be 'killed' in prison, warns wife
-
French court orders release of Lebanese militant held since 1984

-
 Global stocks struggle after Fed signals slower rate cuts
Global stocks struggle after Fed signals slower rate cuts
-
UK economy slows, hitting government growth plans

-
 Primary schools empty as smog persists in Indian capital
Primary schools empty as smog persists in Indian capital
-
Palestinians turn to local soda in boycott of Israel-linked goods

-
 Typhoon Man-yi bears down on Philippines still reeling from Usagi
Typhoon Man-yi bears down on Philippines still reeling from Usagi
-
UK growth slows in third quarter, dealing blow to Labour government

-
 Chris Wood hits quickfire double in NZ World Cup qualifying romp
Chris Wood hits quickfire double in NZ World Cup qualifying romp
-
Markets struggle at end of tough week

-
 China tests building Moon base with lunar soil bricks
China tests building Moon base with lunar soil bricks
-
Film's 'search for Palestine' takes centre stage at Cairo festival

-
 Oil execs work COP29 as NGOs slam lobbyist presence
Oil execs work COP29 as NGOs slam lobbyist presence
-
Gore says climate progress 'won't slow much' because of Trump

| CMSD | 0.01% | 24.36 | $ | |
| CMSC | -0.12% | 24.52 | $ | |
| BCC | -0.12% | 140.175 | $ | |
| RBGPF | 2.67% | 61.84 | $ | |
| RIO | 0.87% | 60.96 | $ | |
| GSK | -2.12% | 33.295 | $ | |
| NGG | 0.24% | 62.52 | $ | |
| SCS | 0.26% | 13.305 | $ | |
| RYCEF | 0.15% | 6.8 | $ | |
| BCE | 0.28% | 26.915 | $ | |
| BTI | 2.33% | 36.335 | $ | |
| JRI | -0.55% | 13.005 | $ | |
| BP | -0.4% | 28.935 | $ | |
| VOD | 0.74% | 8.745 | $ | |
| RELX | -3.46% | 44.415 | $ | |
| AZN | -2.4% | 63.515 | $ |

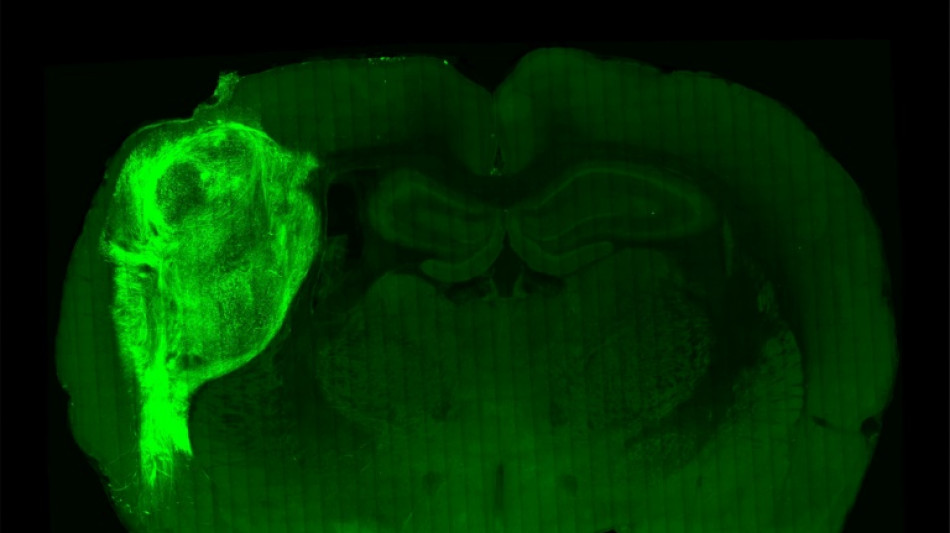
Human brain cells implanted in rats offer research gold mine
Scientists have successfully implanted and integrated human brain cells into newborn rats, creating a new way to study complex psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia and autism, and perhaps eventually test treatments.
Studying how these conditions develop is incredibly difficult -- animals do not experience them like people, and humans cannot simply be opened up for research.
Scientists can assemble small sections of human brain tissue derived from stem cells in petri dishes, and have already done so with more than a dozen brain regions.
But in dishes, "neurons don't grow to the size which a human neuron in an actual human brain would grow", said Sergiu Pasca, the study's lead author and professor of psychiatry and behavioural sciences at Stanford University.
And isolated from a body, they cannot tell us what symptoms a defect will cause.
To overcome those limitations, researchers implanted the groupings of human brain cells, called organoids, into the brains of young rats.
The rats' age was important: human neurons have been implanted into adult rats before, but an animal's brain stops developing at a certain age, limiting how well implanted cells can integrate.
"By transplanting them at these early stages, we found that these organoids can grow relatively large, they become vascularised (receive nutrients) by the rat, and they can cover about a third of a rat's (brain) hemisphere," Pasca said.
- Ethical dilemmas -
To test how well the human neurons integrated with the rat brains and bodies, air was puffed across the animals' whiskers, which prompted electrical activity in the human neurons.
That showed an input connection -- external stimulation of the rat's body was processed by the human tissue in the brain.
The scientists then tested the reverse: could the human neurons send signals back to the rat's body?
They implanted human brain cells altered to respond to blue light, and then trained the rats to expect a "reward" of water from a spout when blue light shone on the neurons via a cable in the animals' skulls.
After two weeks, pulsing the blue light sent the rats scrambling to the spout, according to the research published Wednesday in the journal Nature.
The team has now used the technique to show that organoids developed from patients with Timothy syndrome grow more slowly and display less electrical activity than those from healthy people.
The technique could eventually be used to test new drugs, according to J. Gray Camp of the Roche Institute for Translational Bioengineering, and Barbara Treutlein of ETH Zurich.
It "takes our ability to study human brain development, evolution and disease into uncharted territory", the pair, who were not involved in the study, wrote in a review commissioned by Nature.
The method raises potentially uncomfortable questions -- how much human brain tissue can be implanted into a rat before the animal's nature is changed? Would the method be ethical in primates?
Pasca argued that limitations on how deeply human neurons integrate with the rat brain provide "natural barriers".
Rat brains develop much faster than human ones, "so there's only so much that the rat cortex can integrate".
But in species closer to humans, those barriers might no longer exist, and Pasca said he would not support using the technique in primates for now.
He argued though that there is a "moral imperative" to find ways to better study and treat psychiatric disorders.
"Certainly the more human these models are becoming, the more uncomfortable we feel," he said.
But "human psychiatric disorders are to a large extent uniquely human. So we're going to have to think very carefully... how far we want to go with some of these models moving forward."
W.Moreno--AT