-
 Stock market optimism returns after tech selloff but Wall Street wobbles
Stock market optimism returns after tech selloff but Wall Street wobbles
-
Clarke warns Scotland fans over sky-high World Cup prices

-
 In Israel, Sydney attack casts shadow over Hanukkah
In Israel, Sydney attack casts shadow over Hanukkah
-
Son arrested after Rob Reiner and wife found dead: US media

-
 Athletes to stay in pop-up cabins in the woods at Winter Olympics
Athletes to stay in pop-up cabins in the woods at Winter Olympics
-
England seek their own Bradman in bid for historic Ashes comeback

-
 Decades after Bosman, football's transfer war rages on
Decades after Bosman, football's transfer war rages on
-
Ukraine hails 'real progress' in Zelensky's talks with US envoys

-
 Nobel winner Machado suffered vertebra fracture leaving Venezuela
Nobel winner Machado suffered vertebra fracture leaving Venezuela
-
Stock market optimism returns after tech sell-off

-
 Iran Nobel winner unwell after 'violent' arrest: supporters
Iran Nobel winner unwell after 'violent' arrest: supporters
-
Police suspect murder in deaths of Hollywood giant Rob Reiner and wife

-
 'Angry' Louvre workers' strike shuts out thousands of tourists
'Angry' Louvre workers' strike shuts out thousands of tourists
-
EU faces key summit on using Russian assets for Ukraine

-
 Maresca committed to Chelsea despite outburst
Maresca committed to Chelsea despite outburst
-
Trapped, starving and afraid in besieged Sudan city

-
 Showdown looms as EU-Mercosur deal nears finish line
Showdown looms as EU-Mercosur deal nears finish line
-
Messi mania peaks in India's pollution-hit capital

-
 Wales captains Morgan and Lake sign for Gloucester
Wales captains Morgan and Lake sign for Gloucester
-
Serbian minister indicted over Kushner-linked hotel plan

-
 Eurovision 2026 will feature 35 countries: organisers
Eurovision 2026 will feature 35 countries: organisers
-
Cambodia says Thailand bombs province home to Angkor temples

-
 US-Ukrainian talks resume in Berlin with territorial stakes unresolved
US-Ukrainian talks resume in Berlin with territorial stakes unresolved
-
Small firms join charge to boost Europe's weapon supplies

-
 Driver behind Liverpool football parade 'horror' warned of long jail term
Driver behind Liverpool football parade 'horror' warned of long jail term
-
German shipyard, rescued by the state, gets mega deal

-
 Flash flood kills dozens in Morocco town
Flash flood kills dozens in Morocco town
-
'We are angry': Louvre Museum closed as workers strike

-
 Australia to toughen gun laws as it mourns deadly Bondi attack
Australia to toughen gun laws as it mourns deadly Bondi attack
-
Stocks diverge ahead of central bank calls, US data

-
 Wales captain Morgan to join Gloucester
Wales captain Morgan to join Gloucester
-
UK pop star Cliff Richard reveals prostate cancer treatment

-
 Mariah Carey to headline Winter Olympics opening ceremony
Mariah Carey to headline Winter Olympics opening ceremony
-
Indonesia to revoke 22 forestry permits after deadly floods

-
 Louvre Museum closed as workers strike
Louvre Museum closed as workers strike
-
Spain fines Airbnb 64 mn euros for posting banned properties

-
 Japan's only two pandas to be sent back to China
Japan's only two pandas to be sent back to China
-
Zelensky, US envoys to push on with Ukraine talks in Berlin

-
 Australia to toughen gun laws after deadly Bondi shootings
Australia to toughen gun laws after deadly Bondi shootings
-
Lyon poised to bounce back after surprise Brisbane omission

-
 Australia defends record on antisemitism after Bondi Beach attack
Australia defends record on antisemitism after Bondi Beach attack
-
US police probe deaths of director Rob Reiner, wife as 'apparent homicide'

-
 'Terrified' Sydney man misidentified as Bondi shooter
'Terrified' Sydney man misidentified as Bondi shooter
-
Cambodia says Thai air strikes hit home province of heritage temples

-
 EU-Mercosur trade deal faces bumpy ride to finish line
EU-Mercosur trade deal faces bumpy ride to finish line
-
Inside the mind of Tolkien illustrator John Howe

-
 Mbeumo faces double Cameroon challenge at AFCON
Mbeumo faces double Cameroon challenge at AFCON
-
Tongue replaces Atkinson in only England change for third Ashes Test

-
 England's Brook vows to rein it in after 'shocking' Ashes shots
England's Brook vows to rein it in after 'shocking' Ashes shots
-
Bondi Beach gunmen had possible Islamic State links, says ABC

| SCS | 0.12% | 16.14 | $ | |
| CMSC | -0.04% | 23.291 | $ | |
| RBGPF | -4.49% | 77.68 | $ | |
| RIO | -0.23% | 75.485 | $ | |
| RYCEF | 2.01% | 14.9 | $ | |
| VOD | 1.18% | 12.74 | $ | |
| NGG | 0.93% | 75.63 | $ | |
| BTI | 0.69% | 57.495 | $ | |
| GSK | 0.59% | 49.1 | $ | |
| BCE | 1.07% | 23.6465 | $ | |
| CMSD | 0.21% | 23.3 | $ | |
| RELX | 1.76% | 41.103 | $ | |
| BP | -0.54% | 35.07 | $ | |
| AZN | 1.51% | 91.21 | $ | |
| JRI | 0.1% | 13.58 | $ | |
| BCC | -1.84% | 75.125 | $ |

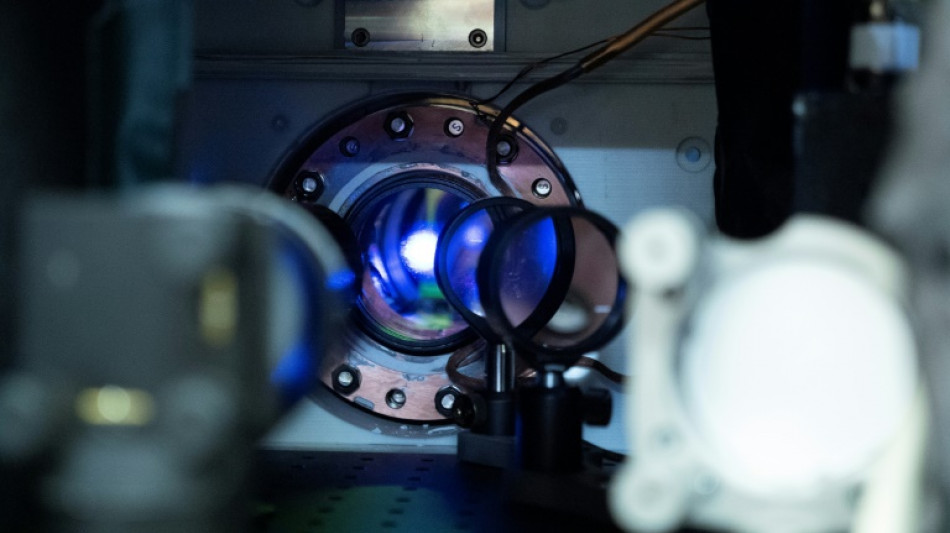
How world's most precise clock could transform fundamental physics
US scientists have measured Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity -- which holds that gravity slows time down -- at the smallest scale ever, demonstrating that clocks tick at different rates when separated by fractions of a millimeter.
Jun Ye, of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Colorado Boulder, told AFP it was "by far" the most precise clock ever built -- and could pave the way for new discoveries in quantum mechanics, the rulebook for the subatomic world.
Ye and colleagues published their findings in the prestigious journal Nature on Wednesday, describing the engineering advances that enabled them to build a device 50 times more precise than their previous best clock, itself a record-breaker, built in 2010.
It was more than a century ago, in 1915, that Einstein put forward his theory of general relativity, which held that the gravitational field of a massive object distorts space-time.
This causes time to move more slowly as one approaches closer to the object.
But it wasn't until the invention of atomic clocks -- which keep time by detecting the transition between two energy states inside an atom exposed to a particular frequency -- that scientists could prove the theory.
Early experiments included the Gravity Probe A of 1976, which involved a spacecraft six thousand miles (10,000 kilometers) above Earth's surface and showed that an onboard clock was faster than an equivalent on Earth by one second every 73 years.
Since then, clocks have become more and more precise, and thus better able to detect the effects of relativity.
A decade ago, Ye's team set a record by observing time moving at different rates when their clock was moved 33 centimeters (just over a foot) higher.
- Theory of everything -
Ye's key breakthrough was working with webs of light, known as optical lattices, to trap atoms in orderly arrangements. This is to stop the atoms from falling due to gravity or otherwise moving, resulting in a loss of accuracy.
Inside Ye’s new clock are 100,000 strontium atoms, layered on top of each other like a stack of pancakes, in total about a millimeter high.
The clock is so precise that when the scientists divided the stack into two, they could detect differences in time in the top and bottom halves.
At this level of accuracy, clocks essentially act as sensors.
"Space and time are connected," said Ye. "And with time measurement so precise, you can actually see how space is changing in real time -- Earth is a lively, living body."
Such clocks spread out over a volcanically-active region could tell geologists the difference between solid rock and lava, helping predict eruptions.
Or, for example, study how global warming is causing glaciers to melt and oceans to rise.
What excites Ye most, however, is how future clocks could usher in a completely new realm of physics.
The current clock can detect time differences across 200 microns -- but if that was brought down to 20 microns, it could start to probe the quantum world, helping bridge gaps in theory.
While relativity beautifully explains how large objects like planets and galaxies behave, it is famously incompatible with quantum mechanics, which deals with the very small, and holds that everything can behave like a particle and a wave.
The intersection of the two fields would bring physics a step closer to a unifying "theory of everything" that explains all physical phenomena of the cosmos.
D.Lopez--AT




